How Did People Tell Time Before Clocks?

Wristwatches became more popular during World War I when they were used by soldiers to keep track of time while in the field. After the war, men's watches became more widely accepted as practical and fashionable accessories. Today, wristwatches are an essential part of men's fashion and are available in a wide range of styles and price points.
Men's watches as we know them today were invented in the late 19th century. The first men's wristwatch was created in 1868 by Patek Philippe, a Swiss watch manufacturer. However, wristwatches were not widely worn by men until the 20th century, when men’s luxury watches became popular as practical and fashionable accessories.
Before the invention of the wristwatch, men carried pocket watches, which were kept in a pocket and were accessed by pulling them out on a chain. Pocket watches were popular in the 16th and 17th centuries and were often worn as a status symbol.
Before the invention of mechanical clocks, people used various methods to tell time. Some of these methods include:
Sundials
A sundial is a device that tells time by using the position of the sun in the sky. It consists of a flat plate called a dial, with lines or markings on it that represent the hours of the day. The sundial also has a gnomon, which is a vertical rod or pole that casts a shadow on the dial. The position of the shadow on the dial indicates the time of day.
There are several types of sundials, including horizontal sundials, vertical sundials, and portable sundials. Horizontal sundials are the most common and are used in gardens and other outdoor spaces. They are placed on a flat surface, such as a table or the ground, and the dial is parallel to the ground. Vertical sundials are placed on a wall or other vertical surface, and the dial is perpendicular to the ground. Portable sundials are small and can be carried in a pocket or purse.
To use a sundial, you must first align it with the north-south line. This can be done by using a compass or by finding the North Star in the night sky. Once the sundial is aligned, you can read the time by looking at the position of the shadow on the dial. Sundials are most accurate at the equinoxes (around March 21 and September 21), when the sun is directly above the equator. They are less accurate at other times of the year, due to the tilt of the earth's axis.
Water Clocks
A water clock, also known as a clepsydra, is a type of clock that uses the flow of water to measure time. It consists of a vessel with a small hole in the bottom, through which water flows at a constant rate. As the water flows out of the vessel, it marks the passage of time on a scale.
Water clocks were used in ancient civilizations, including Egypt, Greece, and China. They were used in temples, public squares, and private homes to tell time. Water clocks were also used to regulate the working hours of slaves and to divide the day into equal parts for astrological purposes.
There are several types of water clocks, including outflow water clocks, inflow water clocks, and float water clocks. Outflow water clocks measure time by the amount of water that flows out of a vessel. Inflow water clocks measure time by the amount of water that flows into a vessel. Float water clocks measure time by the rising and falling of a float in a vessel of water.
Water clocks are less accurate than modern mechanical clocks, as the flow of water can be affected by temperature and other factors. They were eventually replaced by mechanical clocks in the 14th century.
Hourglasses
An hourglass, also known as a sand clock, is a device that uses the flow of sand to measure time. It consists of two glass bulbs connected by a narrow neck, with sand in the middle. When the hourglass is turned over, the sand flows from the upper bulb to the lower bulb through the narrow neck. The time it takes for all the sand to flow from the upper bulb to the lower bulb is used to measure a specific amount of time.
Hourglasses were used in the past as a timing device, particularly on ships. They were used to measure the time it took to complete a specific task or to keep track of how much time had passed. Hourglasses were also used in some religious ceremonies.
Today, hourglasses are not commonly used to tell time, as they are less accurate than mechanical clocks. However, they are still used as decorative objects and can be found in some homes and offices.
Observing Celestial Bodies
Observing celestial bodies refers to the practice of using the position of celestial objects, such as the sun, moon, and stars, to tell time. This method of timekeeping has been used for thousands of years and is still used by some cultures today.
One way to tell time using celestial bodies is to observe the position of the sun in the sky. The sun appears to move across the sky in a predictable pattern, rising in the east, reaching its highest point at noon, and setting in the west. By observing the position of the sun, people were able to divide the day into morning, afternoon, and evening.
The moon can also be used to tell time. The moon orbits the earth and goes through phases, from a new moon to a full moon and back again. By observing the phases of the moon, people were able to mark the passage of time and predict future events, such as the arrival of the next full moon.
Stars were also used to tell time at night. By observing the position of specific stars in the sky, people were able to determine the time of night. Some cultures also used the movement of the stars to predict future events, such as the coming of the rainy season.
Today, celestial bodies are still used to tell the time in some parts of the world, although most people use mechanical clocks or other timekeeping devices.
Mechanical Clocks: Mechanical clocks, which use a system of gears and springs to measure time, were invented in the 14th century. They became more widespread in the 16th and 17th centuries.
Monuments and Architectures
There are several monuments and architecture in India that were designed to tell time using celestial bodies. Some examples include:
Jantar Mantar: Jantar Mantar is a collection of astronomical instruments that were built in the 18th century in several cities across India. It was built by Maharaja Sawai Jai Singh II, who was a patron of science and astronomy. The instruments at Jantar Mantar were used to measure time and predict astronomical events, such as eclipses and the movements of celestial bodies.
There are several different instruments at Jantar Mantar, including sundials, observatories, and other instruments that were used to measure time and predict astronomical events. Some of the instruments at Jantar Mantar include:
Samrat Yantra: The Samrat Yantra is a giant sundial that was used to measure time with great accuracy. It is 90 feet (27 meters) tall and is accurate to within 2 seconds.
Rashivalaya Yantra: The Rashivalaya Yantra is an observatory that was used to measure the positions of celestial bodies. It consists of a series of instruments, including a sextant and a quadrant, that were used to measure the angles of celestial bodies relative to the horizon.
Jayaprakash Yantra: The Jayaprakash Yantra is a set of instruments that were used to measure the positions of celestial bodies and to predict eclipses. It consists of a series of curved metal plates that were used to measure the angles of celestial bodies relative to the horizon.
Jantar Mantar is now a UNESCO World Heritage Site and is a popular tourist destination in India. It is a testament to the scientific traditions of India and is a reminder of the importance of astronomy in ancient cultures.
The Konark Sun Temple: The Konark Sun Temple is a 13th-century temple in the state of Odisha, India. It is dedicated to the sun god Surya and is an important example of Indian temple architecture. The temple features a sundial on its main tower, which was used to tell time. The sundial is a large stone disc with markings on it that represent the hours of the day. The shadow cast by a gnomon (a vertical rod or pole) on the disc indicates the time of day.
The Brihadeeswarar Temple: The Brihadeeswarar Temple is an 11th-century temple in the state of Tamil Nadu, India. It is an important example of Chola architecture and is dedicated to the Hindu god Shiva. The temple has a sundial on the top of its tower, which was used to tell time. The sundial is a large stone disc with markings on it that represent the hours of the day. The shadow cast by a gnomon (a vertical rod or pole) on the disc indicates the time of day.
The Mayo College Observatory: The Mayo College Observatory is a 19th-century observatory in the state of Rajasthan, India. It was built by the British to study celestial bodies and includes a sundial and other instruments used to measure time and predict astronomical events. The observatory is now a museum and is open to the public. It is a testament to the scientific traditions of India and is a reminder of the importance of astronomy in ancient cultures.
There are many other monuments and architectures in India that were designed to tell time using celestial bodies. These structures serve as a testament to the rich history and scientific traditions of India.
Quartz watches for men were invented in the late 1960s. The first quartz watch was the Seiko 35 SQ Astron, which was introduced in Japan in December 1969. Quartz watches use a quartz crystal as a frequency reference to keep time, and they are powered by a battery.
Quartz watches were a major technological breakthrough in the watch industry, as they were much more accurate and affordable than mechanical watches. They quickly gained popularity and became the dominant type of easily accessible watches under 1500 INR in the market.
Water-resistant watches were invented in the early 20th century. The first water resistant watch was made by Rolex and was introduced in 1926. These watches were designed to be worn while swimming and were made with a waterproof case that could withstand some water pressure.
Multifunction trending watches, which are watches that have additional features such as a stopwatch, date display, and alarms, were also invented in the 20th century. The first multifunction watches were introduced in the 1950s and were made by companies such as Timex.
Today, water-resistant and multi function watch is widely available and is popular among consumers. They are used for a variety of purposes, including sports, outdoor activities, and everyday wear.
~Also read:
Recommended Topics
- 2023
- 2024 Collection
- 40mm Dial Watches
- 40mm Men's Watches
- 40mm Watch
- Active Lifestyle
- affordable automatic watch
- Affordable Elegance
- Affordable Watches
- Alarm Setup
- Alarm Watches
- Analog Digital Watches
- Analog vs Smartwatch
- Analog Watches
- analog watches for men
- Anniversary Gifts
- Anniversary Watches
- Automatic Mechanical Watches
- automatic moonstone watch
- automatic watch
- Automatic Watches
- Automatic Watches For Men
- Automatic Watches Under 5000
- Automatic Wrist Watches For Men
- Bella
- Benefits
- Best Blue Dial Watches
- best branded watches under 1000
- Best Casual Watches
- Best Chronograph Watches
- Best Chronograph Watches Under 2000
- best friend gift ideas
- Best Gift For Friend
- Best Low-Price Watches
- Best Metal Watches
- Best of 2024
- Best Picks
- Best Places
- Best Quartz Watches
- Best Selling Watches
- Best Sports Watch
- Best Sports Watches Under 2000
- Best Watch Brands
- Best Watch Brands For Men
- Best Watch Brands For Women
- Best Watch Gift For Boyfriend
- Best Watches
- Best-Dressed Actors
- Birthday Gifts
- Black Analog Watch
- Black Chain Watches
- black dial watch for men
- black dial watch for women
- black dial watches
- black watch for women
- Black Watches
- Blade Watch
- Blue Dial Watches For Ladies
- Blue Watches
- Bollywood Actors
- Boyfriend Watches
- Boys' Watches
- Bracelet Watches
- Bracelet Watches For Women
- Branded Watches
- Branded Watches at Low Price
- branded watches under 1000
- Branded Wrist Watch For Men
- Bride Watches
- Brown Leather Strap Watches
- Budget Friendly
- budget watches
- Budget-Friendly
- budget-friendly watches
- Build and Maintain
- Business Watches
- Buyer's Guide
- Buying Guide
- Casual Watches
- Casual Watches For Men
- Celebration
- Celebrations
- Chain Watch
- chain watches for men
- chain watches for women
- Character
- Christmas 2023
- Christmas Gifts
- Christmas Sale On Watches
- Chrono Watches
- Chronograph watch
- Chronograph Watches
- Chronograph Watches For Men
- Chronograph Watches Under 2000
- Chronograph Watches Under 5000
- circle watch for men & women
- Classic Designs
- Classic to Modern
- Clothing Combo
- Clothing Ideas
- Color Guide
- Commanding Style
- Comparison
- Conscious Consumers
- Consistency
- Cool Casual Watches
- Core Values
- Couple Watches
- Couples
- Craftsmanship
- crystal watch
- Customer Review
- Daily Wear Watches
- Date-Day Watches
- Dazzle vs Serene
- Deployment Clasp
- Diamond Watches
- Diamond Watches For Women
- Digital Watches
- Discounts
- Diva Collection
- Diva Watches
- Dive Watches
- Diwali
- Diwali Festival
- Diwali Gifts
- Diwali Outfits
- Do's and Don'ts
- Dress Watches
- Dressing Style
- Dressing Styles
- Durability
- Dussehra
- Ellore watch
- Elon Musk
- Engraved Messages
- Enthusiasts
- Essential Accessories
- Every Day Watches
- Everyday Look
- Everyday Watches
- Evolution
- Excellence
- Exclusive Watches
- Expensive Watches
- Expert Tips
- Explanation
- Factors
- Facts
- Famous
- Fancy Watches For Men
- Fashion Accessories
- Fashion Models
- Fashion Watches
- Fashionable
- Father's Day
- Festival
- Festival of Colors
- Festive Season
- Formal Watches
- Formal Watches For Men
- formal watches for women
- Free
- Friendship Day
- Frist Sports Watches
- Future of Watches
- Garba Outfits
- Genuine Leather Watch Strap
- gift for women
- Gift Guide
- Gift Ideas
- gift watch
- Gift Watches
- Gifting
- Gifts For Best Friends
- Gifts For Friends
- Gifts for Sisters
- Girl Watches
- Girls' Watches
- Giveaway
- Gold Watches
- Gold Watches For Men
- Gold Watches For Women
- Green Dial Watches
- Groom Watches
- Grooming Tips
- Growth
- Guide
- Handpicked
- Happy Friendship Day
- Hawk Watches
- High-Performance Watches
- high-quality watches
- History
- Holi Sale
- Holiday Gifts
- Holiday Style
- Hollywood Actors
- Hollywood Inspiration
- Hollywood Stars
- How to Know Original Wrist Watch
- How-To
- Husband Watches
- Iconic Collection
- Iconic Watches
- Ideal Selection
- Imperial Collection
- Imperial Watch Collection
- Imperial Watches
- Importance of Time
- Important Rules
- Impress Your Boss
- Indian Cricketers
- Indian Flag
- Indian Politicians
- Indian Watch Brands
- Indian Watch Market
- Indian Watches
- Innovation
- Janmashtami
- Janmashtami 2024
- Japanese
- Job Interview
- Joy of Gifting
- Key Features
- Krishna Janmashtami
- Ladies Fashion Watches
- Ladies Watches
- Latest Trends
- Latest Watches
- Leather Strap
- Leather Strap Watches
- Leather Watch Straps
- Leather Watches
- Light Watch
- Love Language
- Luxurious
- Luxury
- luxury diamond watch for women
- Luxury Gifts For Men
- Luxury Watch Brand
- Luxury Watch Brand For Men
- Luxury Watch Brand For Women
- Luxury Watches
- Luxury Watches For Men
- Maintaining Mechanical Watch
- Maintenance
- Makar Sankranti
- Makar Sankranti 2025
- Makar Sankranti Celebration In India
- Makar Sankranti Wishes
- Marriage Occasion
- Matching Accessories
- Matching Guide
- Materials
- Mechanical Watch Movements
- Mechanical Watches
- Meditation
- Mega Sale
- Men's Accessories
- Men's Blue Dial Watches
- Men's Brown Leather Strap Watches
- Men's Chrono Watches
- Men's Fancy Watches
- Men's Fashion
- Men's Fashion Watches
- Men's Leather Strap Watches
- Men's Outfits
- Men's Roman Numeral Watches
- Men's Style
- Men's Tips
- Men's Watch Styles
- Men's Watches
- Men's Watches With Alarm
- Men’s Water Resistant Watches
- Men’s Wrist Watches
- Metal Watches
- Metal Watches For Men
- Military Watches
- Mind-Body Harmony
- Mindfulness
- minimalist watch
- minimalist watch under 2000
- Minimalist Watches
- Modern Innovations
- Moon Phase Watch
- MoonPhase Watch
- Myths vs. Reality
- National Heroes
- Navratri
- New Features
- New Launch
- New Year's Eve
- Night Watches
- Nylon Strap Watches
- Nylon Watch Straps
- Octagon Shape Watches
- Office Hours
- Office Wear
- Online Buying
- Online Collection
- Online Watches For Women
- Outfit
- Pairing Guide
- Pairing Watches
- Party Wear Watches
- Perfect for Him
- Perfect Gift
- Perfect Watch
- Personality
- Personalized Gifts
- Pre-Wedding Photography
- Premium Brand
- Premium Watch
- Premium Watches
- Premium Watches for Men
- Premium Watches for Women
- Professional Look
- Professional watches
- ProTimer Collection
- Prototype Details
- Prototype Watches
- Quartz Movement
- Quartz vs Automatic
- Quartz Watches
- Quartz Watches For Men
- Race Master
- Racing Watches
- Raksha Bandhan
- Reasons
- Reasons to Wear
- Recommendations
- Republic Collection
- Republic Day
- Rig One 'O One
- Right Watch
- Roman Numeral Watches
- Roman Numeral Watches For Men
- Rose Gold Watches
- Rose Gold Watches For Women
- Rose Gold Women's Watches
- round dial watch
- Round Dial Watches
- round dial watches for women
- Round Shape Watches
- round watch for men
- round watch for women
- Round Watches
- Round Watches For Women
- Rugged Watches
- Santa Sale
- Seasonal Tips
- Self-Love
- September 2023
- Shop Online
- Shopping Tips
- Signature Look
- Significance of Time
- Silicone Strap
- Silicone Watches
- silver strap
- Silver Watches
- Silver Watches For Men
- simple analog watches
- Simplicity
- Situations
- Size Measurement
- Skeleton Watches
- Sleek and Slim
- Slim Watches
- Small Dial Watches
- Small Dial Watches For Ladies
- Small Hands
- Small Watches
- Smartwatches
- Special Gifts for Friend
- Special Occasions
- Special Offers
- Sport Watch
- Sports Fan
- Sports Watches
- Sports Watches For Men
- Square Watches
- Square Watches For Men
- Square Watches For Women
- Stainless Steel Watches
- steel straps
- Stocking Stuffers
- Stopwatch
- Strap For Watches
- Strap watch
- Style
- Style Guide
- Style Statement
- Style Tips
- Styling Tips
- Stylish Watches
- Stylists
- Suit
- Sustainable Watches
- Sylvi Analog Watch
- Sylvi Collection
- Sylvi Insights
- Sylvi Watch
- Sylvi Watches
- Symbolic Watches
- Teachers Day
- Thoughtful Ideas
- Time Carnival
- Time Management
- Time Optimization
- Timekeeping History
- Timeless Appeal
- Timeless Elegance
- Timeless Technology
- Timepieces
- Top 10 Watches
- Top 3 Watches
- Top 4 brown men
- Top Collection
- Top Picks
- Top Watch Brands
- Top Watch Brands in India
- Top Watches
- Traditional Indian Wear
- Traditional Watches
- Traditions
- Transformation
- Travel Watches
- Trendiest Watches
- Trends
- Tribute
- Tricolor Watch Straps
- Types
- Under 1000
- Under 2000
- Unique Features
- Unique Gift
- Unique Ideas
- Unique Watches
- Upgraded
- Valentine Week
- Valentine's Day
- Valuable
- Velocity Watches
- Vibrant Colors
- Vintage Analog Watches
- Vintage Men's Watches
- Vintage Watches
- Vintage Watches For Men
- Vintage Wrist Watches
- Wardrobe
- Watch Advancements
- Watch As a Gift For Boyfriend
- Watch Band
- Watch Battery Life
- Watch Benefits
- watch box
- watch box for gift
- Watch Box Organizer
- Watch Boxes
- Watch Brand In India
- Watch Care
- Watch Care Tips
- Watch Case Size
- Watch Choice
- Watch Clasps
- Watch Collection
- Watch Collection for Men
- Watch Construction
- Watch Details
- Watch Dial Sizes
- Watch Dials
- watch for women under 3000
- Watch Functions
- Watch Gift For Boyfriend
- Watch Gifts
- Watch Ideas
- Watch Mechanics
- Watch Movements
- Watch Pairing
- Watch Pairs
- Watch Parts
- Watch Photography Ideas
- Watch Repair
- Watch Repair Service
- Watch Repair Shop
- Watch Sale
- Watch Selection
- watch store in surat
- watch store near me
- Watch Straps
- Watch Styling
- Watch Trends
- Watch Types
- watch under 2000
- Watch Wearing
- Watch With Light
- Watches
- Watches For Girl
- watches for men
- Watches For Men Low Price
- Watches For Women
- Watches For Women Low Price
- Watches For Women Online
- watches for women under 5000
- watches gift for best friend
- Watches Under 1500
- Watches With Date and Day
- Watches With Sapphire Crystal
- Water Resistance
- Water Resistant Watches
- Water-Resistant
- Waterproof
- Wearing Tips
- Wedding Gift
- Wedding Gifts
- Wedding Watches
- Wedding Watches For Groom
- White Watches
- White Watches For Men
- White Watches For Women
- Winter Watches
- women watches
- Women's Luxury Watches
- Women's Watches
- Women's Watches Online
- Women’s Water Resistant Watches
- World Timer Watch
- World Timer Watches
- Wrist Size Guide
- Wrist Sizes
- Wrist Watch
- Wrist Watches
- Wrist Watches For Men
- Wrists
- Yoga Watches
Latest Watches
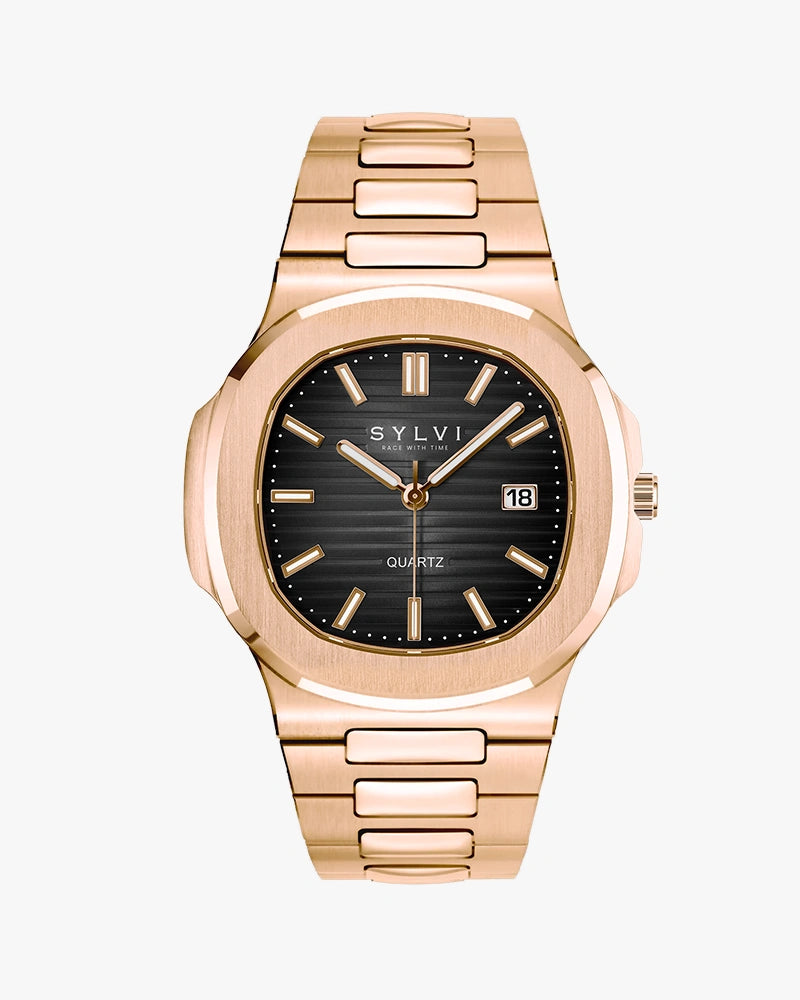
Urbane Rosegold Black
Rs. 2,019.00
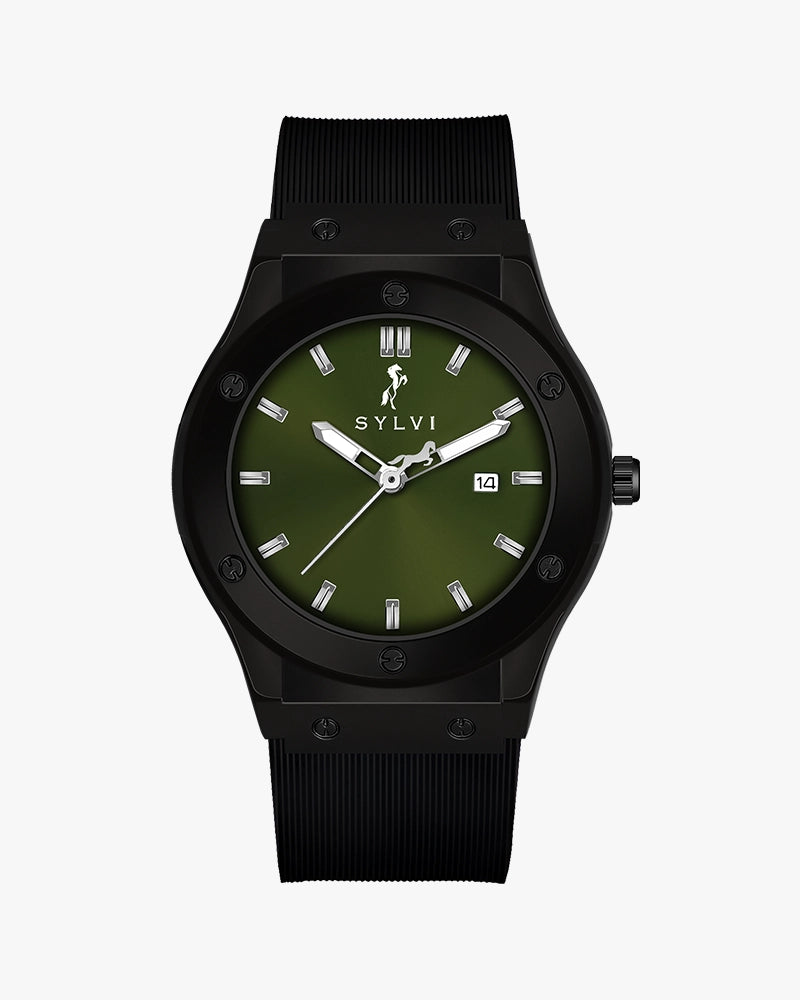
Majestic Green Black Silicone
Rs. 1,749.00
Professional Edge White Rosegold
Rs. 1,799.00
Rig One 'O One White Crystal - WT Max
Rs. 1,679.00



































































Leave a comment